Temperature control is essential for plant growth and health, especially when using a grow tent. The ideal temperature for the grow tent plants is 70-85°F (20-30°C) for healthy growth. If the temperature in a grow tent exceeds 90°F (32°C), severely affects the plant’s growth and kills them.
For this reason, indoor growers utilize different tools and methods to provide enough heat and humidity within an acceptable range. Such methods ensure proper hydration, rich nutrients and continuous photosynthesis for indoor vegetation. Some of the methods include using thermometers, proper thermometer installation, regular temperature checks, and proper air ventilation.
Indoor growers also use the VPD – Vapor Pressure Deficit to calculate the optimal range between the grow room temperature and humidity level. The optimal range of a VPD is 0.8 to 1.2 kPa during the vegetative stage and 1.2 to 1.5 kPa during the flowering stage. This grow room temperature and humidity level ensures a better transpiration rate, improving yields and healthier plants.
Table of Contents
What is the Best Temperature in a Grow Tent?
The ideal temperature for a grow tent largely depends on the specific plants you are cultivating. However, as a general rule, most common indoor plants thrive best in temperatures between 70-85°F (21-29°C) during the light cycle and between 60-75°F (15-24°C) during the dark cycle. The image below briefly describes the ideal temperature for a grow tent.

Photosynthesis – the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy – is most effective within this temperature range. Too high or too low temperatures inhibit photosynthesis, leading to slower growth rates or even plant death.
When the temperature gets too high, above 85°F (30°C), it causes heat stress in your plants. Symptoms of heat stress include wilting, yellowing of leaves, and reduced yield. Extremely high temperatures also increase the risk of pests and diseases, as many pests reproduce more rapidly in hot conditions.
On the other hand, if the temperature drops below 60°F (15°C), it slows down the metabolic processes of your plants, resulting in stunted growth. If temperatures continue to drop, especially below freezing, it kills the plants.
Maintaining an optimal temperature in your grow tent is crucial for the healthy growth of your plants. It’s also important to remember that temperature isn’t the only factor affecting plant growth. Humidity, light intensity, and nutrient availability also play significant roles.
What is the Best Temperature for a LED Grow Tent?
Temperature between 78°F and 85°F (25°C and 29°C) is the best for grow tents. Temperatures between 82 to 85°F (27 to 29°C) are optimal when growing with indoor lights to ensure optimal plant health.
The best flowering temperature for cannabis is 84-85°F (28-29°C). In addition, the best temperature for the atmospheric CO2 levels for most plants with indoor LED lights is 78°F (25°C).
The best temperature for seedlings is between 72 and 82°F (22 and 27°C), while the best temperature for the vegetative state is between 68 and 85°F (20 and 29°C).
What Temperature Should My Grow Room Be When the Lights Are Off?
The best temperature for your grow room, when your lights are off, is between 65°F (18°C) and 68°F (20°C). This temperature is the ideal one as it ensures optimal plant growth.
The main reason for these values is that the temperature of your grow room when the lights are off is cooler than when the lights are on. Plants, like cannabis, experience a natural drop in temperature during their “night” cycle in the wild, and replicating this environment promotes healthy growth. Such grow tent temperature also eliminates the risks of plant stresses.
How Hot Can a Grow Tent Get?
A grow tent can heat up to 95°F (35°C) in an environment with enriched CO2 (more than 1500 PPM), bright LED lights, and low humidity. Indoor grow room plants cannot grow fully this way. For this reason, it is best to keep the temperature in an optimal range – 78 and 85°F (25 and 29°C) to cover all growing stages and ensure full nutrients and health in growing indoor plants.
The temperature inside a grow tent is the highest when the lights are on, especially if you’re using high-heat lighting like HID lamps. These lights emit a significant amount of heat, causing the temperature inside the tent to rise rapidly unless properly ventilated.
The temperature also peaks during the middle of the day when ambient temperatures are typically the highest. Temperature exacerbates if the grow tent is located in a room without air conditioning or proper ventilation.
To manage optimal temperature, growers often use a combination of fans, air conditioning, and exhaust systems to maintain optimal temperatures in the grow tent. They also switch the lights on during cooler parts of the day (like nighttime) to help manage heat levels.
How Hot is Too Hot in a Grow Tent?
If the temperature reaches above 90°F (32°C), it causes severe damage, including wilting, withering, and even death of the plants. When the temperature exceeds 85°F (29°C), it stresses the plants and hinders their growth. The optimal temperature is between 70 to 85°F (21 to 29°C) during the light period and between 60 to 75°F (15 to 24°C) during the dark period is acceptable.
Heat also affects humidity levels, making the environment too dry for your plants. A low tent humidity level leads to problems like nutrient burn and pests. To regulate the temperature in your grow tent, consider using fans, air conditioning units, or other cooling methods. It’s also important to monitor the temperature regularly to ensure it stays within the optimal range.
What Happens When the Temperature Inside the Grow Tent is Too Hot?
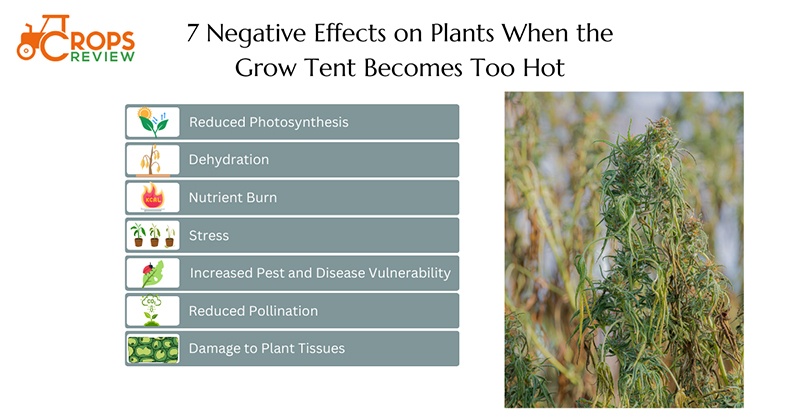
When the temperature inside a grow tent gets too hot, it has 7 negative effects on your plants.
- Reduced photosynthesis: Plants need a certain temperature range for optimal photosynthesis—the process by which they convert light into energy for growth. High temperatures reduce the efficiency of this process, leading to slower growth or even stunted growth.
- Dehydration: High temperatures cause plants to lose water at a faster rate. Dehydration leads to dehydration, wilting, and if not corrected, death of the plant.
- Nutrient burn: High temperatures cause plants to absorb nutrients at a faster rate, leading to nutrient burn. Nutrient burn manifests as yellow or brown discoloration on the leaves.
- Stress: Plants experience stress when conditions are unfavorable like other living organisms. High heat causes stress, leading to slower growth and reduced yield.
- Increased pest and disease vulnerability: High temperatures also create an environment that’s conducive to pests and diseases. Mold, fungi, and pests thrive in warm, humid environments.
- Reduced pollination: In flowering plants, high temperatures affect pollination, reducing the plant’s ability to produce fruit or seeds.
- Damage to plant tissues: Extremely high temperatures directly damage plant tissues, causing leaves to wither and die.
The image below illustrates 7 negative effects on your plants when the grow tent becomes too hot.
To avoid these issues, it’s important to monitor the temperature in your grow tent regularly and take steps to cool it down if necessary, such as improving ventilation, using air conditioning, or installing a cooling system.
Why Does Temperature Control in a Grow Tent Matter?
Temperature control in a grow tent matters for:
Optimal Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light into energy, operates best within specific temperature ranges. If the temperature in your grow tent is too high or too low, it inhibits the process of photosynthesis and affects your plants’ growth and yield.
Prevention of Dehydration: High temperatures cause plants to transpire more rapidly, leading to quicker water loss. By controlling the temperature, you prevent dehydration and ensure your plants have enough moisture to thrive.
Control of Nutrient Uptake: Temperature affects how plants absorb nutrients. Too high temperatures lead to nutrient burn, while too low temperatures slow nutrient uptake.
Stress Minimization: Plants suffer from heat stress or cold stress if temperatures swing too high or too low. Stress results in slower growth, wilting, and in severe cases, death.
Pest and Disease Management: Pests and diseases thrive in specific temperature conditions. By maintaining an optimal temperature, you prevent infestations and keep your plants healthy.
Promotion of Pollination: For plants that bear fruit or flowers, temperature impact the pollination process. Plants require certain temperatures to pollinate properly, and failure to meet these conditions results in reduced yield.
Protection of Plant Tissues: Extreme temperatures directly damage plant tissues, causing them to wither and die. By controlling the temperature in your grow tent, you can protect your plants from such harm.
Temperature control in a grow tent creates the ideal conditions for your plants to grow and thrive, leading to better yields and healthier plants.
Problems With Cold Temps in the Grow Tent
These are the problems cold temperatures in a grow tent cause for plants:
Slowed growth: Plants typically slow their growth in colder conditions, as metabolic processes, including photosynthesis, slow down. Slowed growth results in smaller plants and lower yields.
Stunted seedling development: Young plants and seedlings are particularly susceptible to cold temperatures. Such conditions affect their development and potentially kill them if conditions don’t improve.
Reduced nutrient uptake: Just like high temperatures, low temperatures also interfere with a plant’s ability to absorb nutrients. When it’s too cold, the plant’s roots become less efficient at nutrient uptake, leading to nutrient deficiencies.
Increased risk of disease and pests: Pests and diseases thrive in cold, damp conditions. If your grow tent is too cold, it creates an environment that’s conducive to these problems.
Watering issues: Cold temperatures cause the water in your soil or growing medium to cool, shocking your plants’ roots when watering. Additionally, cold water is less effective at dissolving nutrients, making it harder for plants to get the nutrients they need.
Potential for frost damage: Very cold temperatures result in frost damage. frost causes physical harm to the plant tissues, including cell damage, and in severe cases, kills the plant.
Problems With Hot Temps in the Grow Tent
Hot temperatures in a grow tent lead to severe issues for your plants, such as
Inhibited photosynthesis: High temperatures hinder the photosynthesis process, which is vital for plant growth. The slower process of photosynthesis results in slower or stunted growth.
Dehydration: Heat increases the rate of evaporation, causing plants to lose water quickly. Water loss leads to dehydration, wilting, and, death.
Nutrient burn: When it’s too hot, plants absorb nutrients too quickly, causing a nutrient burn. The phenomenon of nutrient burn often appears as yellow or brown discoloration on the leaves.
Heat stress: Plants experience stress under high heat conditions, slowing growth, reducing yield, and making them more susceptible to disease.
Increased pest and disease activity: Pests and diseases are active in hot, humid conditions. Such conditions mean a hot grow tent leads to an increased risk of infestation.
Reduced pollination: For flowering plants, high temperatures affect the pollination process, inhibiting the plant’s ability to produce fruit or seeds.
Damage to plant tissues: Extreme heat damage plant cells and tissues, causing leaves to wither and die.
To prevent these problems, it’s important to maintain an optimal temperature in your grow tent. Achieve the optimal temperature range by using air conditioning, improving ventilation, or installing a cooling system.
How to Measure Temperature in a Grow Tent?
Here are 4 main steps on how to measure temperature in a grow tent:
1. Invest in quality thermometers: You need a good thermometer to measure the temperature in your grow tent. Both analog and digital thermometers work, but many growers prefer digital versions because they’re often easier to read and more accurate. Digital thermometers also come with separate sensors to measure temperatures from outside the grow tent, which is helpful when the lights are off.
2. Place thermometers strategically: One thermometer isn’t enough. Place multiple thermometers throughout your grow tent to get a more accurate reading of the overall temperature. Key locations include the top of the canopy, outside of the canopy, and on the opposite wall. Place a thermometer near the base of a plant and in the soil or growing medium.
3. Avoid direct light: Place the thermometer away from direct light to prevent the light from artificially raising the thermometer’s reading.
4. Check temperature regularly: Regularly check the temperature readings on your thermometers to monitor the conditions in your grow tent. Make necessary adjustments to maintain the ideal temperature for your plants.

Maintaining the right temperature in your grow tent is crucial for healthy plant growth and maximizing yield. By accurately measuring the temperature, you ensure your plants have the best possible growing environment.
Where to Put a Temperature Probe in Grow Tent?
Put a temperature probe in a grow tent in the proper places, such as:
Canopy level: The most common advice is to place the temperature probe at the canopy level. The canopy level is the area where your plants’ leaves are growing and is therefore the most critical area to monitor. The probe is shaded from direct light as infrared radiation affects the readings.
Center of the tent: Positioning your probe in the center of your grow tent, below the light at canopy level provides an accurate reading of the overall temperature in your tent.
Near the top of the tent: Place a temperature sensor near the top of the grow tent, as this area often has a higher-than-average temperature due to heat rising.
Under the canopy near the pots: As the plants get larger, keep a probe under the canopy near the pots. This zone is crucial for plant growth when the root zone temperature is staying within an optimal range.
Away from direct airflow: Ensure that the probe is not directly in the path of a fan or air conditioner to avoid skewed readings.
How to Heat a Grow Tent in Winter?
These are 6 methods to heat a grow tent in winter: use a space heater, insulate your grow tent, adjust your lighting schedule, improve air circulation, use ducting to insulate your grow tent, place your grow tent in direct sunlight. The figure below illustrates those 6 ways.
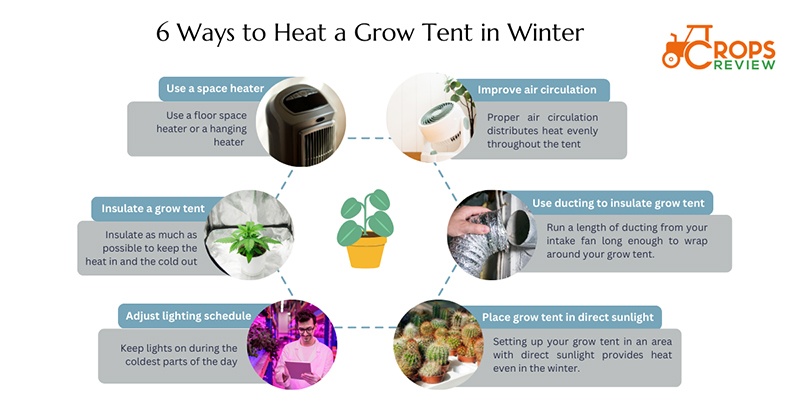
Use a space heater. A floor space heater or a hanging heater is often used inside the grow tent. Make sure to monitor the temperature regularly to prevent overheating while using your best heater for grow tent.
Insulate your grow tent. Insulate as much as possible to keep the heat in and the cold out. Insulation involves wrapping your tent with blankets, building insulation, water heater insulation, or even spray foam. Placing your grow tent on a carpet or rug instead of a cold floor also adds a layer of insulation.
Adjust your lighting schedule with the best light for grow tent such as LED lights. Keep lights on during the coldest parts of the day. The lights you use for growing generate heat that warms up your tent.
Improve air circulation. Proper air circulation distributes heat evenly throughout the tent. Use fans to improve air circulation.
Use ducting to insulate your grow tent. Run a length of ducting from your intake fan long enough to wrap around your grow tent.
Place your grow tent in direct sunlight. Setting up your grow tent in an area with direct sunlight provides heat even in the winter.
Monitor the ideal temperature in your grow tent regularly to ensure it stays within the optimal range for your plants. Overheating your grow tent can be just as damaging as too-cold temperatures, as plants cannot grow properly due to a lack of nutrients and worsening environmental conditions.
How to Cool Grow Tent Temperature?
You can cool grow tent temperature in 5 ways, such as a ventilation fan for grow tent, DIY cooling methods, a portable air conditioner, chiller, an air conditioner and a dehumidifier.
- Use a ventilation fan for grow tent to regulate the temperature by circulating air inside the grow tent, reducing the overall heat.
- Use DIY methods such as salt, water, ice, a Styrofoam cooler, and a small inline fan to create a makeshift cooling system.
- Apply a portable air conditioner in the same room as your grow tent to help control the cool air circulating in the space.
- Use a chiller since it works similarly to a refrigerator, maintaining the nutrient solution at an optimal temperature, which can help manage the issue during the summer.
- Use air conditioners and dehumidifiers to help you cool your grow space, as they provide optimal temperature levels: 70-85°F (20-30°C), and humidity levels 75-85% for all growing stages, seedlings, vegetative and flowering stages.
What Are the Factors That Affect Temperature in the Grow Tent?
These are the main 7 factors that affect the temperature in a grow tent: Lighting, ventilation, room temperature, humidity, size of the grow tent, number and size of plants, and seasons/weather.
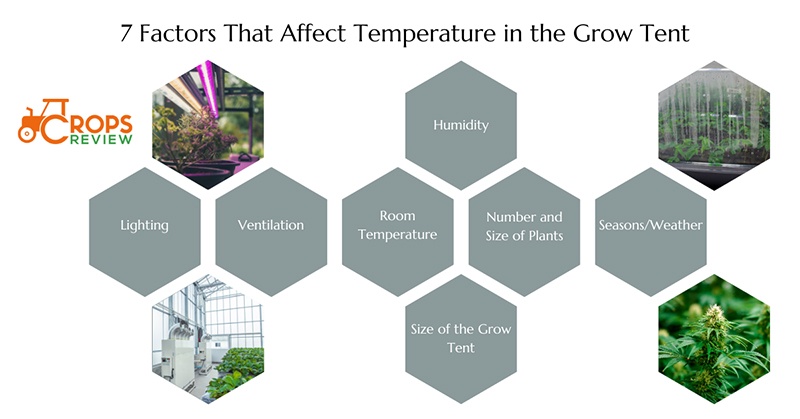
- Lighting: The type and intensity of lighting used in a grow tent significantly impacts its temperature. For example, High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lights, such as metal halide and high-pressure sodium, generate more heat compared to LED or fluorescent lights.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining ideal temperatures in a grow tent. Without adequate airflow, heat builds up quickly, causing temperatures to rise. It’s important to have a good extraction fan and possibly an intake fan to keep the air circulating.
- Room temperature: The ambient temperature of the room where the grow tent is located also affects the temperature inside the tent. If the room is too hot or cold, it causes the grow tent temperature to rise or fall accordingly.
- Humidity: Higher humidity makes the environment feel warmer, while lower humidity makes it feel cooler, which also causes the loss of nutrients and affects the proper growth of plants.
- Size of the grow tent: Smaller tents heat up quicker than larger ones. In a larger tent, heat is spread over a larger area to keep temperatures down.
- Number and size of plants: More plants or larger plants lead to higher humidity levels and temperatures due to transpiration.
- Seasons/weather: The time of year and the weather significantly affect your grow tent’s temperature. Winter months make it hard to keep the indoor growing tent warm, while summer months lead to higher temperatures and even overheating.
Are Grow Tents Insulated?
Grow tents are not typically insulated. They are designed to provide a controlled environment for plants, but tents don’t have insulation properties to maintain temperature.
However, growers add insulation to grow tents to help control the temperature and humidity conditions more effectively, especially in colder climates. Insulation is achieved using various materials like blankets, foam board insulation, or even special grow tent insulation materials available in DIY stores (foam board, bubble wrap, thermal shedding, etc.).
VPD: Relation Between Temperature and Humidity
VPD, or Vapor Pressure Deficit, is a measure of the difference (deficit) between the amount of moisture in the air and how much moisture the air holds when it is saturated for optimal humidity in grow tent.
VPD is crucial as plants transpire, or “breathe”, through tiny openings on their leaves called stomata. When the VPD is too high (air is too dry), plants close their stomata to prevent excess water loss, hindering their ability to take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Conversely, when the VPD is too low (air is too humid), the rate of transpiration decreases, and plants become more susceptible to diseases due to the moist conditions. By controlling the VPD in a grow room or tent, you optimize the rate of transpiration, leading to healthier plants and better yields.
The optimal range of a VPD is 0.8 to 1.2 kPa during the vegetative stage and 1.2 to 1.5 kPa during the flowering stage.
